|
A Comprehensive Guide to Safe Biological Pest Control |
* Ask a Question * |
| Home About FAQ Quick Reference | |
NATURAL BIOLOGICAL FLY CONTROL WITH FLY PARASITES
SMALL FLY PARASITES WILL ELIMINATE FLIES
We provide 3 species of predatory fly parasites: Spalangia cameroni, Muscidifurax zaraptor and Muscidifurax raptorellus.
All three species working together are more affective in eliminating flies.
Fly Parasites are gnat-sized, nocturnal, burrowing insects which do not bite, or sting humans and animals. Adaptable to all climates, these parasites reproduce in one to two weeks, thus constantly replenishing the beneficial insect population. The fly Parasites are the naturally occurring enemy of all manure breeding pest flies. In nature these tiny insect predators serve as a major check of fly populations by destroying flies in the immature maggot and pupa stages. Fly Parasite are specific to flies, never attacking anything else. It's important to realized that these tiny wasps have absolutely no effect on horses or humans. They stay close to the manure and dirt where filty pest, and even if they could reach you or your horse, the fly parasite are so small that they cannot sting. Their main purpose in life is to act as a natural predator against filty flies and they do a great job. Fly Parasites are a preferred alternative to chemical insecticides that are hazardous to human and animal life. NO ADVERSE SIDE EFFECTS. A major benefit of biological control is that it avoids completely the adverse side effects of chemical sprays, such as poison residue in the environment affecting not only the pests but also non-target animals (songbirds, beneficial insects, etc.) and most importantly your domestic stock. This is a serious problem as some of the common spray residues are effective for up to 3 or 4 years, and remember that poisonous toxic chemicals become less effective with repeated use.
| Fly Parasite Control:
Fly Parasites, the natural enemy Beneficial Nematodes |
Fly Managment Program
- Remove manure regularly. |
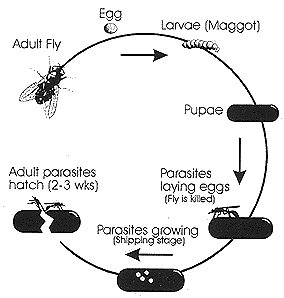
Parasite Particulars
 |
|
Parasite Application
Your insects arrive in a bag as parasitized pupae in a sawdust medium. The pupae are at various stages of development. Store at room temperature away from dogs and ants. Check for hatching over the next day or two by holding the bag up to a light source. When the first gnat-like parasites appear inside the bag it's time for application. Once dispersed, hatching will continue over the next week.
The parasites are nocturnal, thus the optimal release time is dusk. Apply the parasites around the edges of "hot spots" areas where manure and urine are accumulated - where flies are crawling and breeding. Scratch a 1/2" hole in the ground with your heel, drop in a tablespoon of the sawdust and pupae mixture, and cover the hole with dirt, manure, or straw. Repeat this process every 10-20 feet until the package contents are gone. Use a little extra in problem "hot spots".
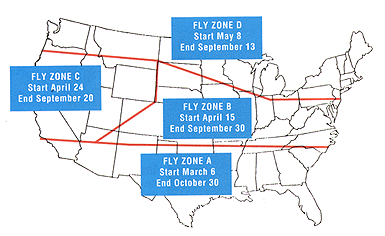
Buglogical has designed a Fly Control Program using regular releases of fly parasites and beneficial nematodes. First, use regular releases of fly parasites based upon the prescriptions to the right. Second, use beneficial nematodes once or twice a year to treat manure piles or any areas where fly larvae populations may be abundant. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
